IT/모바일
제공 : 한빛 네트워크
저자 : 임영규, 대한상공회의소 충북인력개발원 정보통신과 교수
USB를 이용하는 경우 일반적으로 USB2Serial 컨버트를 사용한다. 이 경우 실제 USB 스펙이 제공하는 통신 속도를 모두 활용하지 못하고 Serial에 의존적인 통신을 하게 된다.
오픈소스인 libusb의 윈도우 버전인 libusb-win32를 사용하여 USB를 효율적으로 사용하는 방법을 알아본다.
먼저 sourceforge.net에서 libusb-win32 패키지를 다운로드 한다.
그리고 다음 절차에 따라 INF 파일을 생성하고 드라이버를 등록, 프로그램에서 액세스하는 과정을 따른다
1. 인스톨 INF 위저드를 실행하여 USB 직접 통신을 하고자 하는 디바이스의 INF 파일을 만드는 과정이다. inf-wizard.exe 프로그램을 실행하면 다음과 같은 진행 과정이 나타난다
2. 그림에서 어느 USB를 사용할 것인지를 선택한다. 필자의 경우 USB serial C/V를 선택했다.
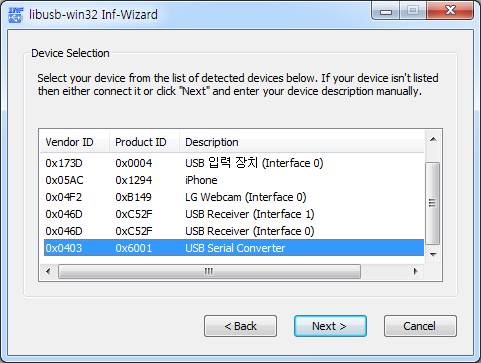
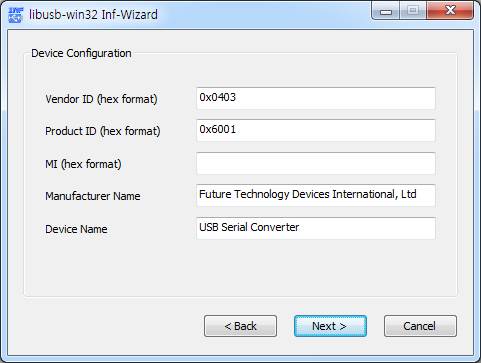
3. 다음 과정은 선택한 USB의 V(endor ID) P(roduct ID)를 찾아서 보여주며 이것은 프로그램에서 직접 사용하게 됨으로 VID, PID를 기록해 둔다. 이 정보를 기반으로 USB 통신을 하게 된다
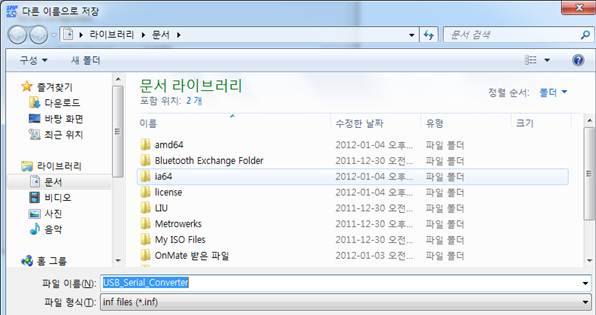
4. 이제 INF 파일을 저장할 경로를 선택한다
5. INF 파일이 저장되었기 때문에 해당 드라이버를 설치할 것인지를 선택하게 된다. 만약 설치 하지 않는 경우 Done을 클릭하고, 원할 경우 만들어 둔 INF 파일을 선택하고 우클릭해서 설치를 하면 된다
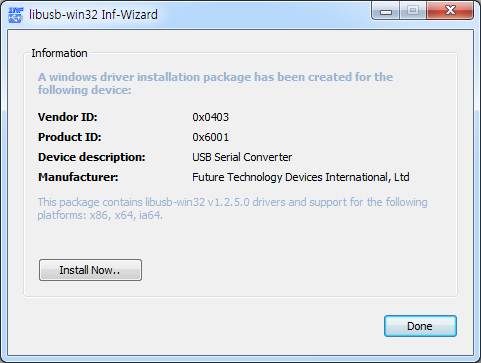
설치 과정은 이미 설치된 드라이버를 검색한 다음 설치하기 때문에 약간의 시간을 필요로 한다.
6. 마지막으로 예제 파일을 오픈하여 원하는 코드를 작성하는 과정이다.
7. 예제 프로그램
Example 폴더에 예제 프로그램이 있다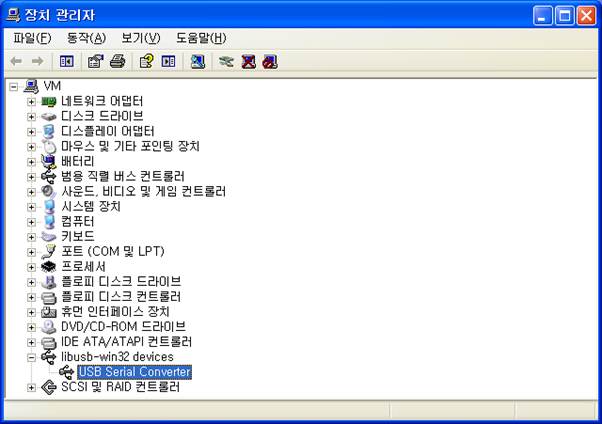
디바이스 설치가 완료되면 위와 같이 장치관리자에 USB 장치가 등록되는데 이름은 libUSB-win32로 되어있다.
중요한 것은 INF 파일 생성 과정 중에 기록해 둔 VID와 PID를 소스 내에 삽입해야 하는데, 위 예제에서 다음 라인을
저자 : 임영규, 대한상공회의소 충북인력개발원 정보통신과 교수
USB를 이용하는 경우 일반적으로 USB2Serial 컨버트를 사용한다. 이 경우 실제 USB 스펙이 제공하는 통신 속도를 모두 활용하지 못하고 Serial에 의존적인 통신을 하게 된다.
오픈소스인 libusb의 윈도우 버전인 libusb-win32를 사용하여 USB를 효율적으로 사용하는 방법을 알아본다.
먼저 sourceforge.net에서 libusb-win32 패키지를 다운로드 한다.
그리고 다음 절차에 따라 INF 파일을 생성하고 드라이버를 등록, 프로그램에서 액세스하는 과정을 따른다
1. 인스톨 INF 위저드를 실행하여 USB 직접 통신을 하고자 하는 디바이스의 INF 파일을 만드는 과정이다. inf-wizard.exe 프로그램을 실행하면 다음과 같은 진행 과정이 나타난다
2. 그림에서 어느 USB를 사용할 것인지를 선택한다. 필자의 경우 USB serial C/V를 선택했다.

3. 다음 과정은 선택한 USB의 V(endor ID) P(roduct ID)를 찾아서 보여주며 이것은 프로그램에서 직접 사용하게 됨으로 VID, PID를 기록해 둔다. 이 정보를 기반으로 USB 통신을 하게 된다

4. 이제 INF 파일을 저장할 경로를 선택한다

5. INF 파일이 저장되었기 때문에 해당 드라이버를 설치할 것인지를 선택하게 된다. 만약 설치 하지 않는 경우 Done을 클릭하고, 원할 경우 만들어 둔 INF 파일을 선택하고 우클릭해서 설치를 하면 된다

설치 과정은 이미 설치된 드라이버를 검색한 다음 설치하기 때문에 약간의 시간을 필요로 한다.
6. 마지막으로 예제 파일을 오픈하여 원하는 코드를 작성하는 과정이다.
7. 예제 프로그램
Example 폴더에 예제 프로그램이 있다
#include#include // Enables this example to work with a device running the // libusb-win32 PIC Benchmark Firmware. #define BENCHMARK_DEVICE ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // TEST SETUP (User configurable) // Issues a Set configuration request #define TEST_SET_CONFIGURATION // Issues a claim interface request #define TEST_CLAIM_INTERFACE // Use the libusb-win32 async transfer functions. see // transfer_bulk_async() below. #define TEST_ASYNC // Attempts one bulk read. #define TEST_BULK_READ // Attempts one bulk write. // #define TEST_BULK_WRITE ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // DEVICE SETUP (User configurable) // Device vendor and product id. #define MY_VID 0x0666 #define MY_PID 0x0001 // Device configuration and interface id. #define MY_CONFIG 1 #define MY_INTF 0 // Device endpoint(s) #define EP_IN 0x81 #define EP_OUT 0x01 // Device of bytes to transfer. #define BUF_SIZE 64 ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// usb_dev_handle *open_dev(void); static int transfer_bulk_async(usb_dev_handle *dev, int ep, char *bytes, int size, int timeout); usb_dev_handle *open_dev(void) { struct usb_bus *bus; struct usb_device *dev; for (bus = usb_get_busses(); bus; bus = bus->next) { for (dev = bus->devices; dev; dev = dev->next) { if (dev->descriptor.idVendor == MY_VID && dev->descriptor.idProduct == MY_PID) { return usb_open(dev); } } } return NULL; } int main(void) { usb_dev_handle *dev = NULL; /* the device handle */ char tmp[BUF_SIZE]; int ret; void* async_read_context = NULL; void* async_write_context = NULL; usb_init(); /* initialize the library */ usb_find_busses(); /* find all busses */ usb_find_devices(); /* find all connected devices */ if (!(dev = open_dev())) { printf("error opening device: %s ", usb_strerror()); return 0; } else { printf("success: device %04X:%04X opened ", MY_VID, MY_PID); } #ifdef TEST_SET_CONFIGURATION if (usb_set_configuration(dev, MY_CONFIG) < 0) { printf("error setting config #%d: %s ", MY_CONFIG, usb_strerror()); usb_close(dev); return 0; } else { printf("success: set configuration #%d ", MY_CONFIG); } #endif #ifdef TEST_CLAIM_INTERFACE if (usb_claim_interface(dev, 0) < 0) { printf("error claiming interface #%d: %s ", MY_INTF, usb_strerror()); usb_close(dev); return 0; } else { printf("success: claim_interface #%d ", MY_INTF); } #endif #ifdef TEST_BULK_WRITE #ifdef BENCHMARK_DEVICE ret = usb_control_msg(dev, USB_TYPE_VENDOR | USB_RECIP_DEVICE | USB_ENDPOINT_IN, 14, /* set/get test */ 2, /* test type */ MY_INTF, /* interface id */ tmp, 1, 1000); #endif #ifdef TEST_ASYNC // Running an async write test ret = transfer_bulk_async(dev, EP_OUT, tmp, sizeof(tmp), 5000); #else // Running a sync write test ret = usb_bulk_write(dev, EP_OUT, tmp, sizeof(tmp), 5000); #endif if (ret < 0) { printf("error writing: %s ", usb_strerror()); } else { printf("success: bulk write %d bytes ", ret); } #endif #ifdef TEST_BULK_READ #ifdef BENCHMARK_DEVICE ret = usb_control_msg(dev, USB_TYPE_VENDOR | USB_RECIP_DEVICE | USB_ENDPOINT_IN, 14, /* set/get test */ 1, /* test type */ MY_INTF, /* interface id */ tmp, 1, 1000); #endif #ifdef TEST_ASYNC // Running an async read test ret = transfer_bulk_async(dev, EP_IN, tmp, sizeof(tmp), 5000); #else // Running a sync read test ret = usb_bulk_read(dev, EP_IN, tmp, sizeof(tmp), 5000); #endif if (ret < 0) { printf("error reading: %s ", usb_strerror()); } else { printf("success: bulk read %d bytes ", ret); } #endif #ifdef TEST_CLAIM_INTERFACE usb_release_interface(dev, 0); #endif if (dev) { usb_close(dev); } printf("Done. "); return 0; } /* * Read/Write using async transfer functions. * * NOTE: This function waits for the transfer to complete essentially making * it a sync transfer function so it only serves as an example of how one might * implement async transfers into thier own code. */ static int transfer_bulk_async(usb_dev_handle *dev, int ep, char *bytes, int size, int timeout) { // Each async transfer requires it"s own context. A transfer // context can be re-used. When no longer needed they must be // freed with usb_free_async(). // void* async_context = NULL; int ret; // Setup the async transfer. This only needs to be done once // for multiple submit/reaps. (more below) // ret = usb_bulk_setup_async(dev, &async_context, ep); if (ret < 0) { printf("error usb_bulk_setup_async: %s ", usb_strerror()); goto Done; } // Submit this transfer. This function returns immediately and the // transfer is on it"s way to the device. // ret = usb_submit_async(async_context, bytes, size); if (ret < 0) { printf("error usb_submit_async: %s ", usb_strerror()); usb_free_async(&async_context); goto Done; } // Wait for the transfer to complete. If it doesn"t complete in the // specified time it is cancelled. see also usb_reap_async_nocancel(). // ret = usb_reap_async(async_context, timeout); // Free the context. usb_free_async(&async_context); Done: return ret; }

디바이스 설치가 완료되면 위와 같이 장치관리자에 USB 장치가 등록되는데 이름은 libUSB-win32로 되어있다.
중요한 것은 INF 파일 생성 과정 중에 기록해 둔 VID와 PID를 소스 내에 삽입해야 하는데, 위 예제에서 다음 라인을
TAG :
이전 글 : 기업을 위한 오픈 소스 커뮤니티 협업 전략
다음 글 : 빅 데이터와 시민권에 대하여
최신 콘텐츠
